Video Tutorial: Creating a Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK) Cluster
Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK)
Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK) is a fully managed Kafka distribution optimized for Kubernetes environments. It provides a comprehensive set of features for deploying, managing, and scaling Kafka clusters with ease.
Key Features
- Managed Kafka: Simplifies Kafka operations with automated deployment, scaling, and management.
- Integration with Confluent Platform: Seamlessly integrates with Confluent’s ecosystem, including Schema Registry, KSQL, and Connect.
- Kubernetes Native: Designed specifically for Kubernetes, leveraging its capabilities for resource management and scaling.
- Monitoring and Management: Provides built-in monitoring and management tools for Kafka clusters, including metrics and logs.
- Security:
- Supports TLS encryption, authentication, and authorization.
- Integrates with Kubernetes RBAC for fine-grained access control.
- Multi-Cloud Support: Can be deployed across multiple cloud providers, ensuring high availability and disaster recovery.
How to Deploy CFK
Deploying Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK) using Streamtime is straightforward and can be done through the Streamtime UI.
What StreamTime Creates for You
- CFK Components: Kafka brokers with KRaft, Schema Registry (if enabled), Control Center.
- Kubernetes Objects: Namespaces, Deployments/StatefulSets, Services (LB/ClusterIP), PersistentVolumeClaims.
- Networking: LoadBalancers/ingress according to your Outbound Access and Private Access choices.
- Storage: Block Volumes‑backed Persistent Volumes sized per your config.
Prerequisites
-
A Kubernetes Fleet
Before you can create a CFK cluster, ensure that you have a Kubernetes Fleet already bootstrapped on any supported cloud platform using StreamTime. How to deploy A Kubernetes fleet. -
Bootstrap Provider Permissions for Tiered Storage Setup
A Bootstrap Provider configured with an user that has permission to create Object Storage buckets for Tiered Storage and Users for granting access to the created bucket. If the bucket is already created, the user will need permissions to create a credentials (Ex - Access Key in AWS, Customer Secret Key in OCI) and have access to the bucket.
Steps to Create a CFK Cluster in StreamTime
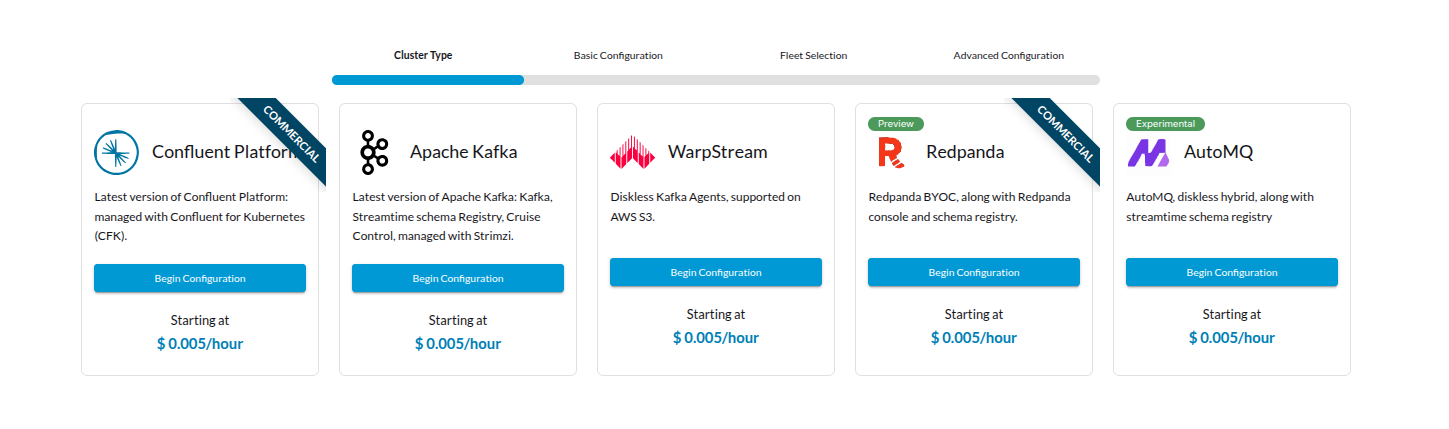
Step-1: Select Cluster Type
Navigate to Clusters → Create Cluster → select Confluent Platform (Commercial) → Click Begin Configuration.
Step-2: Basic Configuration
Configure the sizing and placement of your CFK cluster.

- Identifier
- Human-readable cluster ID
- You can use the auto-generated identifier or provide your own, which must be unique per organization. (Auto-generated names are provided only for UI convenience and not intended for real-world cluster names, hence use meaningful identifiers)
- Example:
clickstream-pipe
- Tags
- Key/value labels applied to StreamTime objects
- Useful for environment, owner, cost-center, etc.
- Example:
environment=non-prod
- Cloud Provider
- Target cloud for deployment
- Guidance: Choose any cloud provider of your choice (Example shown for OCI)
- Region
- OCI region where the Fleet is created
- Must match an existing Fleet region
- Example:
ap-hyderabad-1
- Tenancy
- Defines the resource sharing model
- Options: Shared, Dedicated or Isolated, Refer to the docs on Tenancy
- Kafka Units (KU)
- Baseline throughput capacity
- Each KU ≈ 20 MB/s aggregate
- Alert Channels
- Health and incident notifications
- Optional; choose Slack/Email channels configured in Settings
Sizing Tip- 1 KU (~20 MB/s) is good for dev/test or light prod. For production with replication factor = 3 and bursty writes, consider higher suitable KU to avoid broker IO saturation.
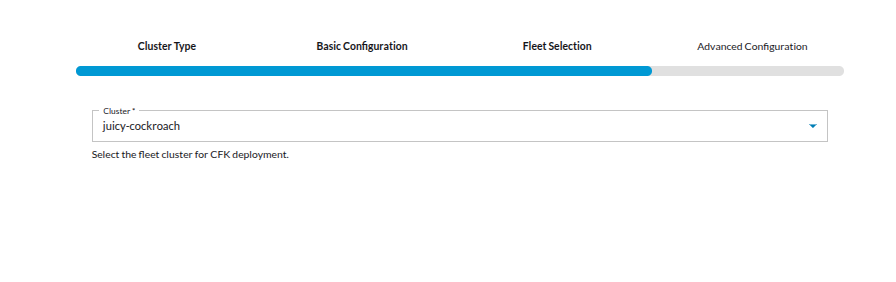
Step‑3: Fleet Selection (This step applies only to Administrator users.)
- Select the Kubernetes Fleet that will host this CFK cluster.
- Choose preferred Kubernetes cluster for deploying Confluent Platform.
- This ensures that StreamTime deploys the Confluent Platform inside your existing Kubernetes fleet.
Step-4: Advanced Configuration (This step applies only to Administrator users.)
Fine‑tune networking, security, components, and storage.

-
Optimization Goal
You have three choices for controlling how the cluster manages egress networking (traffic going out of the cluster):- Cost → Optimized for lowest cost.
- Limits or routes outbound traffic through shared, cheaper paths.
- Best for dev/test clusters where traffic is light.
- Balanced (default) → Mix between performance and cost.
- Suitable for most production environments.
- Provides decent throughput with moderate costs.
- Performance → Optimized for maximum throughput and lowest latency.
- Uses premium networking resources.
- Best for high-throughput, latency-sensitive production workloads.
- Cost → Optimized for lowest cost.
-
Cluster Access
Controls how clients connect to Kafka brokers:- Internal → Only accessible within the Kubernetes cluster (ideal for private, secure setups where client workloads run in the same cluster).
- External → Accessible from outside the Kubernetes cluster (needed when clients run outside the cluster).
- Internal & External → Both internal and external clients can connect.
-
Authentication Mechanism
Defines how clients authenticate to Kafka:- SASL/OAUTH → OAuth-based authentication.
- More secure, integrates with identity providers.
- Recommended by StreamTime.
- SASL/PLAIN → Username/password-based authentication.
- Simpler but less secure.
- SASL/OAUTH → OAuth-based authentication.
- Additional System Admin
You can assign extra system administrators who will have full access to manage the CFK cluster.
-
Additional System Admin Type
Specifies the type of principal mentioned in Additional System Admin. If the admin name provided is a group in the identity provider, set the Additional System Admin Type as Group, else, set it as user -
Storage Tier Configuration
Defines how Kafka tiered storage manages log segment offloading to tiered storage:-
Aggressive → Offloads data to tiered storage quickly, keeping local disk usage minimal.
(Suitable when you want to optimize for cost and use cloud storage heavily) -
Balanced → Default option. Keeps a healthy balance between local disk and tiered storage usage.
-
Conservative → Keeps data locally for longer before offloading to tiered storage.
- (Useful if you want faster local access and rely less on cloud storage)
- (Requires larger local disk size, which increases infrastructure cost.)
-
- Tiered Storage Bucket Name
The name of the Object Storage bucket which will be used for tiered storage. Ensure that this is globally unique for a provider.
Tip: Use a naming convention that is unique for your organization and use numbers to ensure global uniqueness.
-
Tiered Storage Provider
All Confluent Platform clusters created by StreamTime have Tiered Storage enabled for lowering storage costs. Learn more hereChoose where offloaded Kafka data will be stored:
- AWS
- AWS Account → Your AWS account identifier configured as a Bootstrap Provider in the Organization Settings. Ensure the user configured for this Provider has the following policy -
{ "Version" : "2012-10-17", "Statement" : [ { "Effect" : "Allow", "Action" : [ "s3:*" ], "Resource" : "<bucket-name>" } ] } - Region → The AWS region where your S3 bucket exists.
- AWS Account → Your AWS account identifier configured as a Bootstrap Provider in the Organization Settings. Ensure the user configured for this Provider has the following policy -
- OCI
-
OCI Account → Your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure account ID (Tenancy OCID).
Your OCI account identifier configured as a Bootstrap Provider in the Organization Settings. Ensure the user configured for this Provider has the following policy -
Allow group <group-name> to manage buckets in compartment id <compartment-id>Allow group <group-name> to manage objects in compartment id <compartment-id> - Region → The OCI region where the bucket exists.
- Compartment ID → OCID of the compartment where the storage bucket resides.
-
- AWS
Once all steps are complete-
- Review the configuration shown on the right side of the screen.
- Click Create Cluster.
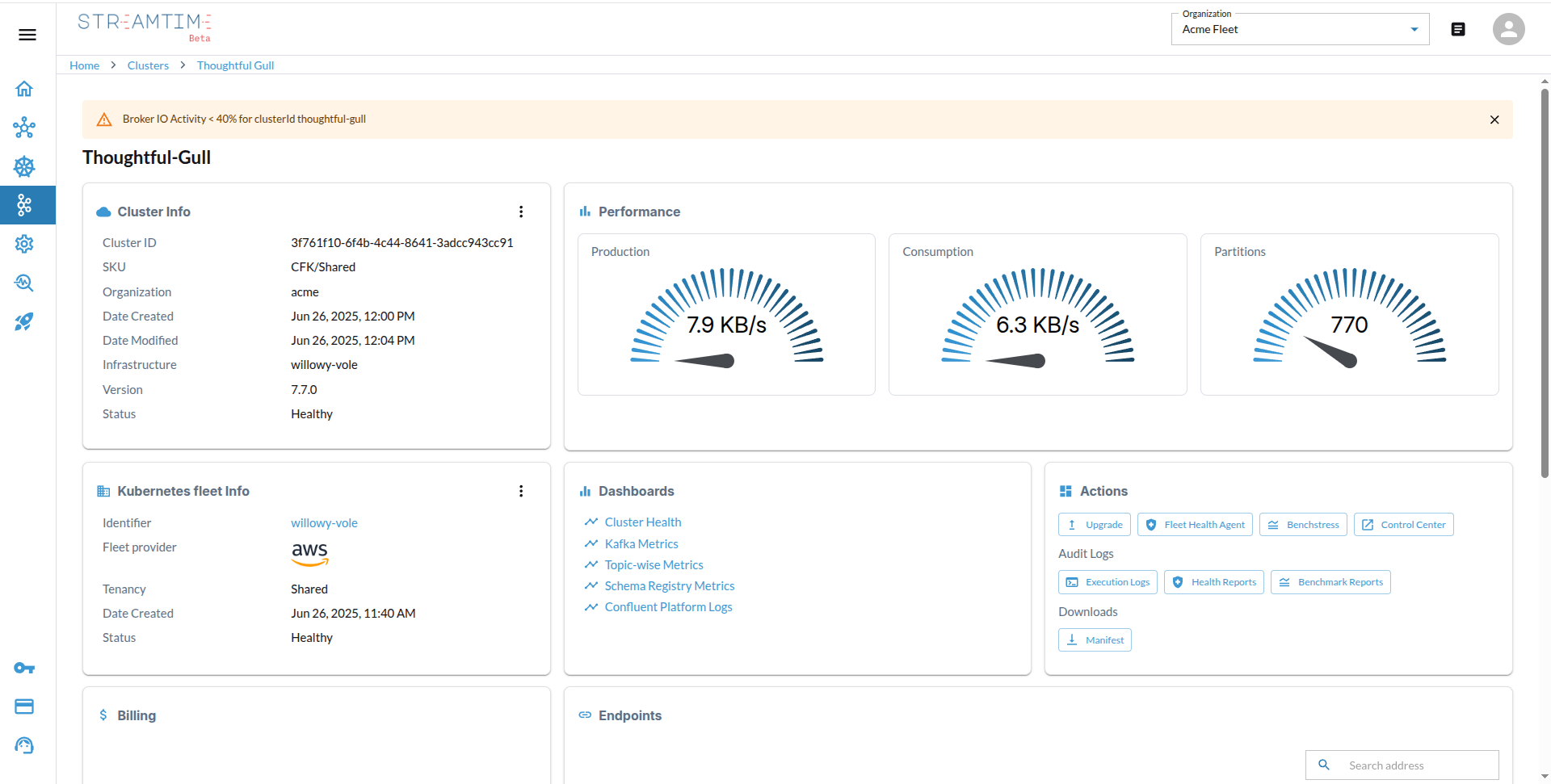
Monitoring and Management
- Metrics Dashboards: Visualize key metrics such as throughput, latency, and error rates.
- Logs: Access Kafka logs for troubleshooting and auditing.
- Alerts: Set up alerts for critical events and performance issues.
- Scaling: Easily scale the Kafka cluster by adjusting the number of Kafka units or adding more nodes to the underlying Kubernetes fleet.
API Reference
Create a Confluent for Kubernetes (CFK) Cluster
curl -X POST https://<streamtime-api-endpoint>/organizations/<your-org-id>/clusters/ \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"identifier": "working-wallaby",
"cluster_type": "cfk",
"kafka_units": 3,
"provisioner_name": "",
"tenancy_mode": "Shared",
"advanced_config": {
"cluster_access": "Internal & External",
"authentication_mechanism": "SASL/OAUTH",
"private_access": false,
"version": "7.7.0",
"auto_upgrade_version": false,
"node_count": 3,
"oauth": "okta-dev-47119201",
"additional_system_admin": "Administrators",
"additional_system_admin_type": "group",
"storage_tier_configuration": "Balanced",
"tiered_storage_bucket_name": "cluster-cfk-404",
"tiered_storage_provider": {
"aws_account": "platformatory",
"aws_region": "us-east-1"
},
"tiered_storage_create_bucket": true
},
"tags": [
{
"key": "environment",
"value": "non-prod"
}
],
"organization": "<your-org-id>",
"cloud_provider": "aws",
"region": "us-east-1",
"infrastructure": "sympathetic-emu"
}'
Response:
{
"id": "cdc0647e-51cc-458f-9fdc-6ea31143b95b",
"organization": "<your-org-id>",
"infrastructure": "sympathetic-emu",
"identifier": "working-wallaby",
"provisioner_name": "",
"destroyer_name": null,
"version_updater_name": null,
"cluster_type": "cfk",
"tenancy_mode": "Shared",
"kafka_units": 3,
"cloud_provider": "aws",
"region": "us-east-1",
"tags": [
{
"key": "environment",
"value": "non-prod"
}
],
"advanced_config": {
"cluster_access": "Internal & External",
"authentication_mechanism": "SASL/OAUTH",
"private_access": false,
"version": "7.7.0",
"auto_upgrade_version": false,
"node_count": 3,
"oauth": "okta-dev-47119201",
"additional_system_admin": "Administrators",
"additional_system_admin_type": "group",
"storage_tier_configuration": "Balanced",
"tiered_storage_bucket_name": "cluster-cfk-404",
"tiered_storage_provider": {
"aws_account": "platformatory",
"aws_region": "us-east-1"
},
"tiered_storage_create_bucket": true
},
"console_url": null,
"client_properties": null,
"new_version": null,
"s3_manifests_file_path": null,
"status": "Pending",
"created_at": "2025-07-17T09:54:37.723465Z",
"updated_at": "2025-07-17T09:54:37.723481Z"
}