Bootstrapping on Oracle (OKE)
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is supported as a bootstrap provider for creating Kubernetes fleets in Streamtime, enabling you to deploy and manage Kafka clusters on Oracle Kubernetes Engine (OKE) with integrated automation.
Prerequisites:
1. Before you can create a Kubernetes fleet in **StreamTime, you need a user that belongs to a group with the right level of permissions in OCI.**
- Create a Group in OCI for StreamTime users (e.g., streamtime-admins).
- Add your user to this group.
-
Attach a policy to the group that grants the required permissions. The policy should include the following statement:
Allow group <group-name> to manage all-resources in compartment id <compartment-id>
This ensures that StreamTime can provision, manage, and monitor all OCI resources (compute, networking, storage, and OKE clusters) within the specified compartment.
2. Generate an API key for the user. Refer to the official documentation- Managing API Keys
Steps to Create a Bootstrap Provider on Oracle in StreamTime
Step-1: Create a Bootstrap Provider Navigate to Settings → Bootstrap Providers → Select OCI OKE → Next

Step-2: Fill in the Configuration Form
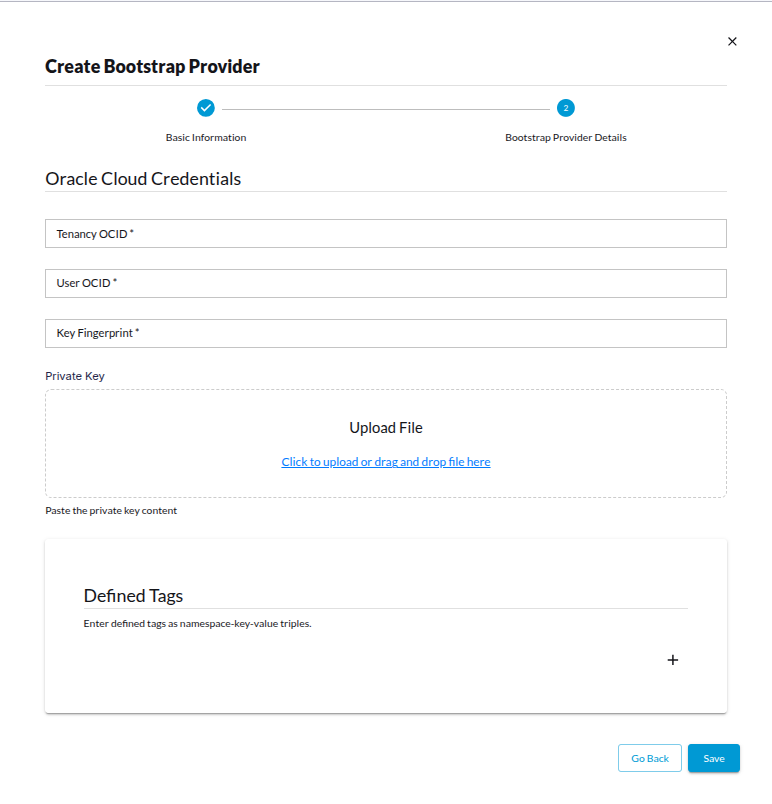
- Tenancy OCID – OCID of the OCI Tenancy in which the resources should be created.
- User OCID – OCID of the IAM user StreamTime will use to create and manage resources.
- Key Fingerprint – Fingerprint of the above user’s API key.
- Private Key – Paste the PEM private key that matches the API key.
-
Defined Tags – Tags that StreamTime will automatically apply to every OCI resource it provisions (compute, networking, storage, OKE). Enter tags as
namespace.key=value. Using defined tags ensures consistent ownership, cost allocation, governance, and auditing across all StreamTime-created resources. When you create the tag key definition, you choose its value type, which determines how users assign values to resources. StreamTime automatically applies these defined tags to all resources it creates in OCI. You can add multiple tags, ensuring that every compute, network, and storage resource provisioned through StreamTime is consistently tagged under your chosen namespace, making it easier to:- Track resource ownership and usage
- Align deployments with cost centers or projects
- Enforce governance policies
- Simplify reporting and auditing across your environment
- Identity Domain OCID – OCID of the OCI Identity Domain for creating an user for object storage bucket access. If not provided, the default domain in the tenancy is used. This is required in scenarios where the user does not have access to the default Identity Domain and needs to use a different Identity Domain.
By defining and applying these tags at the StreamTime level, you get end-to-end visibility and control over your OCI resources without needing to manually tag them later.
Learn more about defined tags in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
When to Use Oracle (OKE)
- Oracle Cloud Preference: When your workloads or data reside primarily in OCI.
- OKE Features: If you want to leverage Oracle’s managed Kubernetes capabilities.
- Enterprise Integration: For organizations using Oracle Cloud services and databases.
- Regional Compliance: When you need to deploy clusters in specific OCI regions for compliance or latency.
Key Features
- Managed Kubernetes (OKE): Automated provisioning and management of OKE clusters.
- Flexible Tenancy: Support for shared, isolated, or dedicated tenancy models.
- Integrated Security: Leverage OCI IAM and security features.
- Scalable Throughput: Define Kafka units and scale clusters as needed.
- Placement Options: Deploy in any supported OCI region.
How to Deploy on Oracle (OKE)
Prerequisites:
- An OCI account with appropriate permissions.
- API keys configured in Streamtime for OCI access.
- A defined compartment in OCI where the fleet will live.
- A Base Domain is required (you can add it in the Settings Panel).
- (Optional) SSH key for accessing worker nodes.
Steps to Create a OKE on StreamTime
Step-1:Bootstrap provider selection
Navigate to Bootstrap Providers → Add Kubernetes Fleet → Select OCI OKE

Step-2: Basic Configuration Basic Configuration step with fields for Identifier, Tenancy, Base Domain, Alert Channels, and sliders for Max Tenants and Max Kafka Units
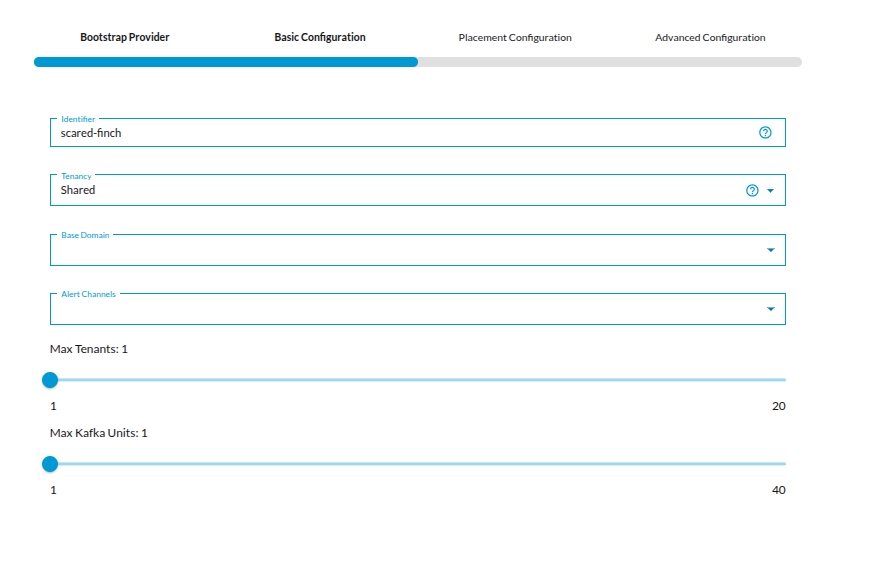
-
Identifier
-
A unique name you assign to your Kubernetes fleet (Use the auto-generated name or provide your own unique name. Here it is
scared-finch). -
Must be unique within your account.
-
-
Tenancy
- Defines how resources are shared, refer the docs for more information Tenancy in Streamtime
-
Base Domain
-
The root domain used for accessing services in the fleet.
-
For example: if you set example.com, your workloads will be exposed as service.example.com.
-
The Base Domain must be configured prior to fleet creation if it’s not already set in the Settings panel., Refer to the docs on Domains
-
-
Alert Channels
-
Where Streamtime will send alerts for fleet events (scaling issues, failures, upgrades, etc.).
-
Can be things like Slack channels, Email etc
-
-
Max Tenants
-
The maximum number of tenants (kafka clusters) that can be hosted in this fleet.
-
Example: If you set 5, you can host up to 5 different tenants (clusters) on this fleet.
-
-
Max Kafka Units
-
The maximum Kafka capacity units (a resource abstraction Streamtime uses for sizing Kafka clusters).
-
One “Kafka Unit” typically maps to a certain amount of broker resources (CPU, memory, storage, throughput). Refer, Scaling Kafka Clusters in Streamtime
-
Setting this defines how much Kafka workload this fleet can handle.
-
Example: If you set 10, tenants can request Kafka resources up to 10 units in total.
-
Step-3: Placement Configuration

- Account
-
This is the OCI account you already onboarded into Streamtime (via API keys).
-
Example: data-platform-oci (your configured account).
-
- Region
-
The OCI region where your Kubernetes fleet (and Kafka Cluster cluster) will be deployed.
-
Example: ap-hyderabad-1.
-
- Compartment OCID
-
You must paste the OCID of the OCI compartment where your Kubernetes resources should live.
-
This decides which compartment Streamtime will use to spin up the fleet/cluster.
-
Navigate to: Identity & Security → Compartments → [Your Compartment] → OCID
-
Looks like: ocid1.compartment.oc1..aaaaaaaexampleuniqueID12345
In the OCI Console, you can locate your Compartment OCID by navigating to:
OCI Console → Identity & Security → Compartments → [Your Compartment] → OCID
-
Step-4: Advanced Configuration
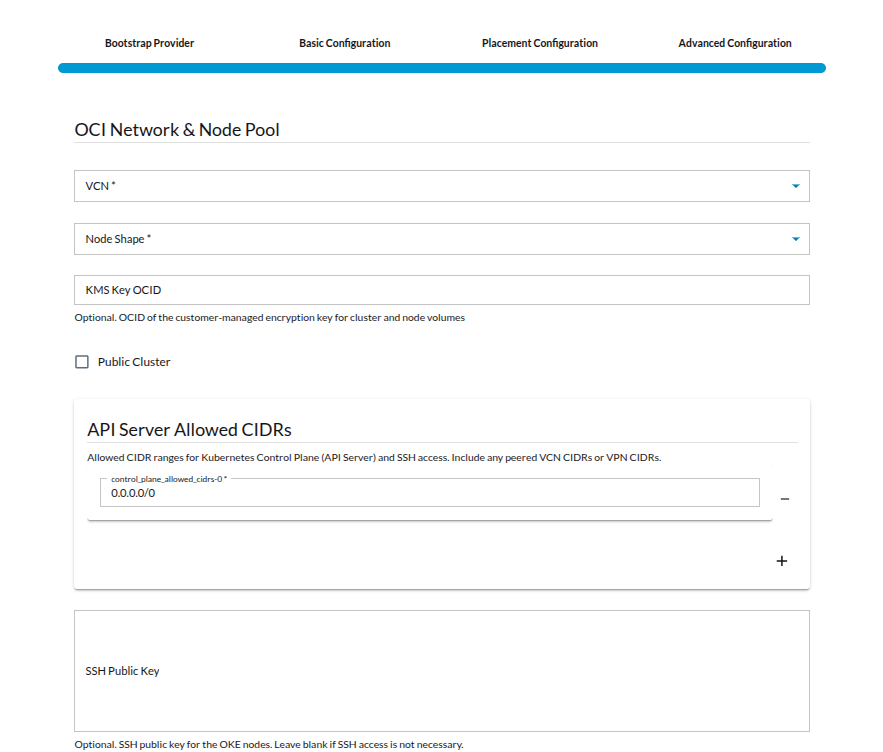
-
VCN (Virtual Cloud Network)
-
The VCN provides the networking backbone for your Kubernetes fleet, including subnets for both the control plane and worker nodes.
-
You can create a new VCN or select an existing VCN from your OCI account.
-
Streamtime will use this VCN to allocate IP addresses, route traffic, and manage network security for the cluster.
Tip: Ensure the VCN has enough IP address space for all nodes and services in your fleet.
-
- Node Shape
- This defines the compute instance shape for worker nodes
-
KMS Key OCID (Optional)
- KMS Key OCID (Optional): If you have a customer-managed encryption key stored in OCI Vault, you can specify its OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier) here. This key will be used to securely encrypt your Kubernetes cluster data and node volumes, providing an additional layer of data protection and control over encryption keys. If you choose to leave this field blank, Oracle-managed encryption keys will be used by default, meaning Oracle handles all encryption management without requiring you to specify a custom key. Using a customer-managed key gives you greater control over key lifecycle, rotation, and access, enhancing your overall security posture.
-
Public Cluster(Checkbox)
-
If checked, the Kubernetes API server endpoint will be publicly accessible.
-
If unchecked, it will be private and accessible only within the VCN.
-
-
API Server Allowed CIDRs
-
These are CIDR ranges allowed to access the Kubernetes API server (control plane) and for SSH into worker nodes.
-
Example shown: 0.0.0.0/0 → This means the API server is open to all IPs (security risk).
-
Best practice: Restrict to your office IP or VPN CIDR (e.g., 203.x.x.x/32).
-
-
SSH Public Key
- Here you can provide your SSH public key.
-
This allows you to SSH into the OKE worker nodes.
- If left blank, you won’t be able to SSH into nodes directly (still manageable via Kubernetes API).